Overview of the Palo Alto Networks PCNSE Exam
The Palo Alto Networks PCNSE exam assesses an individual's understanding of Palo Alto Networks next-generation firewalls and their ability to manage, monitor, and troubleshoot these devices effectively. The exam covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Firewall fundamentals
- Threat prevention
- Network security
- Device management
- Cloud Security
To prepare for the PCNSE exam, candidates should have a strong understanding of network security concepts and technologies. DumpsBoss offers comprehensive PCNSE exam preparation materials, including practice tests, study guides, and flashcards, to help candidates succeed on their first attempt.
Definition of MTU
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the largest size of a data frame or packet that can be transmitted over a particular network interface. MTU is measured in bytes and is typically set to the smallest common denominator of all the network interfaces on a path between two hosts.
If a data frame or packet is larger than the MTU, it will be fragmented into smaller pieces before being transmitted. Fragmentation can add overhead to the network and can slow down performance. Therefore, it is important to set the MTU to the optimal value for the network.
The optimal MTU can be determined by using the following formula:
MTU = MSS + IP header size + TCP header size + Ethernet header size
Where:
- MSS is the maximum segment size for TCP
- IP header size is 20 bytes
- TCP header size is 20 bytes
- Ethernet header size is 14 bytes
For example, if the MSS is 1460 bytes, the optimal MTU would be 1514 bytes.
DumpsBoss offers a variety of resources to help network administrators learn more about MTU and how to set it optimally. These resources include articles, tutorials, and practice tests.
The Network Layer and MTU
The network layer is the third layer of the OSI model and is responsible for routing data packets between hosts on a network. The network layer also provides services such as error checking and flow control.
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the largest size of a data packet that can be transmitted over a particular network interface. MTU is measured in bytes and is typically set to the smallest common denominator of all the network interfaces on a path between two hosts.
If a data packet is larger than the MTU, it will be fragmented into smaller pieces before being transmitted. Fragmentation can add overhead to the network and can slow down performance. Therefore, it is important to set the MTU to the optimal value for the network.
The optimal MTU can be determined by using the following formula:
MTU = MSS + IP header size + TCP header size + Ethernet header size
Where:
- MSS is the maximum segment size for TCP
- IP header size is 20 bytes
- TCP header size is 20 bytes
- Ethernet header size is 14 bytes
For example, if the MSS is 1460 bytes, the optimal MTU would be 1514 bytes.
DumpsBoss offers a variety of resources to help network administrators learn more about MTU and how to set it optimally. These resources include articles, tutorials, and practice tests.
How the Network Layer Uses MTU
The network layer uses the maximum transmission unit (MTU) to determine the largest size of a data packet that can be transmitted over a particular network interface. The MTU is typically set to the smallest common denominator of all the network interfaces on a path between two hosts.
If a data packet is larger than the MTU, it will be fragmented into smaller pieces before being transmitted. Fragmentation can add overhead to the network and can slow down performance. Therefore, it is important to set the MTU to the optimal value for the network.
The network layer uses the following process to determine the optimal MTU for a particular path:
- The source host sends a data packet to the destination host with a "don't fragment" bit set.
- If the packet reaches the destination host without being fragmented, then the MTU is the largest possible value.
- If the packet is fragmented, then the source host reduces the MTU by the size of the fragment and sends the packet again.
- The source host repeats steps 2 and 3 until the packet reaches the destination host without being fragmented.
Once the optimal MTU has been determined, the source host will continue to send data packets with the "don't fragment" bit set. This will ensure that the packets are not fragmented and will reach the destination host as quickly as possible.
DumpsBoss offers a variety of resources to help network administrators learn more about MTU and how to set it optimally. These resources include articles, tutorials, and practice tests.
MTU and Palo Alto Networks Firewalls
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the largest size of a data packet that can be transmitted over a particular network interface. MTU is measured in bytes and is typically set to the smallest common denominator of all the network interfaces on a path between two hosts.
Palo Alto Networks firewalls use MTU to determine the largest size of a data packet that can be transmitted through the firewall. The firewall will fragment packets that are larger than the MTU into smaller pieces before transmitting them. Fragmentation can add overhead to the network and can slow down performance. Therefore, it is important to set the MTU to the optimal value for the network.
The optimal MTU for a Palo Alto Networks firewall can be determined by using the following formula:
MTU = MSS + IP header size + TCP header size + Ethernet header size
Where:
- MSS is the maximum segment size for TCP
- IP header size is 20 bytes
- TCP header size is 20 bytes
- Ethernet header size is 14 bytes
For example, if the MSS is 1460 bytes, the optimal MTU would be 1514 bytes.
DumpsBoss offers a variety of resources to help network administrators learn more about MTU and how to set it optimally for Palo Alto Networks firewalls. These resources include articles, tutorials, and practice tests.
Best Practices for Managing MTU in Networks
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the largest size of a data packet that can be transmitted over a particular network interface. MTU is measured in bytes and is typically set to the smallest common denominator of all the network interfaces on a path between two hosts.
Best practices for managing MTU in networks include:
- Set the MTU to the optimal value for the network. The optimal MTU can be determined by using the following formula:
MTU = MSS +
IP header size + TCP header size + Ethernet header size
Where:
* MSS is the maximum segment size for TCP
* IP header size is 20 bytes
* TCP header size is 20 bytes
* Ethernet header size is 14 bytes
<p>* **Use jumbo frames.** Jumbo frames are data packets that are larger than the standard MTU of 1500 bytes. Jumbo frames can improve performance on networks with high bandwidth and low latency.</p>
<p>* **Fragment packets if necessary.** If a data packet is larger than the MTU,
it will need to be fragmented into smaller pieces before being transmitted. Fragmentation can add overhead to the network and can slow down performance. However, it is sometimes necessary to fragment packets in order to get them to their destination.
Monitor the network for MTU-related problems. MTU-related problems can include packet loss, high latency, and slow performance. If you are experiencing any of these problems, you should check the MTU settings on your network devices.
DumpsBoss offers a variety of resources to help network administrators learn more about MTU and how to manage it effectively. These resources include articles, tutorials, and practice tests.
Final tips for PCNSE exam preparation
Here are some final tips to help you prepare for the Palo Alto
Networks PCNSE exam:
- Review the exam blueprint. The exam blueprint is a document that outlines the topics that will be covered on the exam. It is important to review the blueprint carefully so that you can focus your studies on the most important topics.
- Use DumpsBoss practice tests. DumpsBoss offers a variety of practice tests that can help you assess your knowledge of the PCNSE exam topics. The practice tests are designed to be challenging and will help you identify areas where you need to improve your knowledge.
- Join a study group. Studying with other people can be a great way to learn and retain information. Joining a study group can also help you stay motivated and on track with your studies.
- Get enough sleep. It is important to get enough sleep in the days leading up to the exam. Getting enough sleep will help you stay focused and alert during the exam.
- Eat a healthy breakfast. Eating a healthy breakfast on the day of the exam will help you stay energized and focused.
- Arrive at the testing center early. Arriving at the testing center early will help you relax and get settled in before the exam starts.
- Stay calm and confident. It is important to stay calm and confident during the exam. If you start to feel nervous, take a few deep breaths and focus on the questions one at a time.
Good luck with your PCNSE exam!
Special Discount: Offer Valid For Limited Time “PCNSE Exam” Order Now!
Sample Questions for Palo Alto Networks PCNSE Dumps
Actual exam question from Palo Alto Networks PCNSE Exam.
After switching to a different WAN connection, users have reported that various websites will not load, and timeouts are occurring. The web servers work fine from other locations.
The firewall engineer discovers that some return traffic from these web servers is not reaching the users behind the firewall. The engineer later concludes that the maximum transmission unit (MTU) on an upstream router interface is set to 1400 bytes.
The engineer reviews the following CLI output for ethernet1/1.
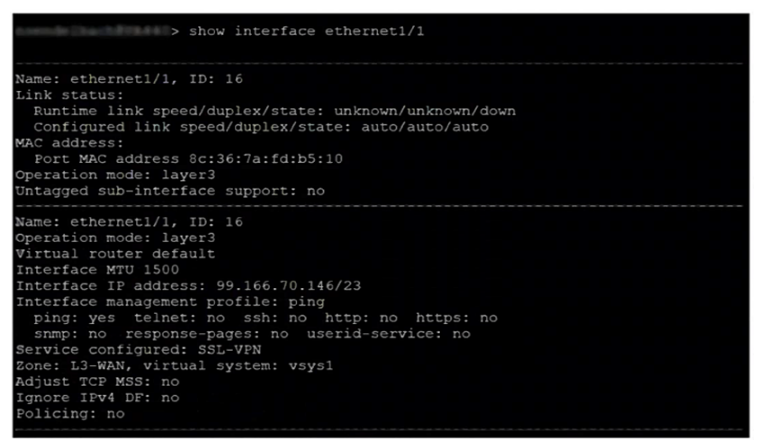
Which setting should be modified on ethernet1/1 to remedy this problem?
A. Change the subnet mask from /23 to /24.
B. Lower the interface MTU value below 1500.
C. Adjust the TCP maximum segment size (MSS) value.
D. Enable the Ignore IPv4 Don't Fragment (DF) setting.


